AMD’s recent financial disclosures reveal a powerhouse of growth and potential that defies conventional expectations. With a record-breaking revenue of $7.7 billion — a 32% increase compared to the same period last year — the company is positioning itself as a formidable player in the semiconductor industry. This surge isn’t merely fueled by a transient market trend but demonstrates AMD’s strategic prowess in capturing consumer enthusiasm and enterprise demand alike. Its core segments, particularly Client and Gaming, showcase remarkable resilience and innovation, effectively challenging longstanding industry giants like Intel and Nvidia.
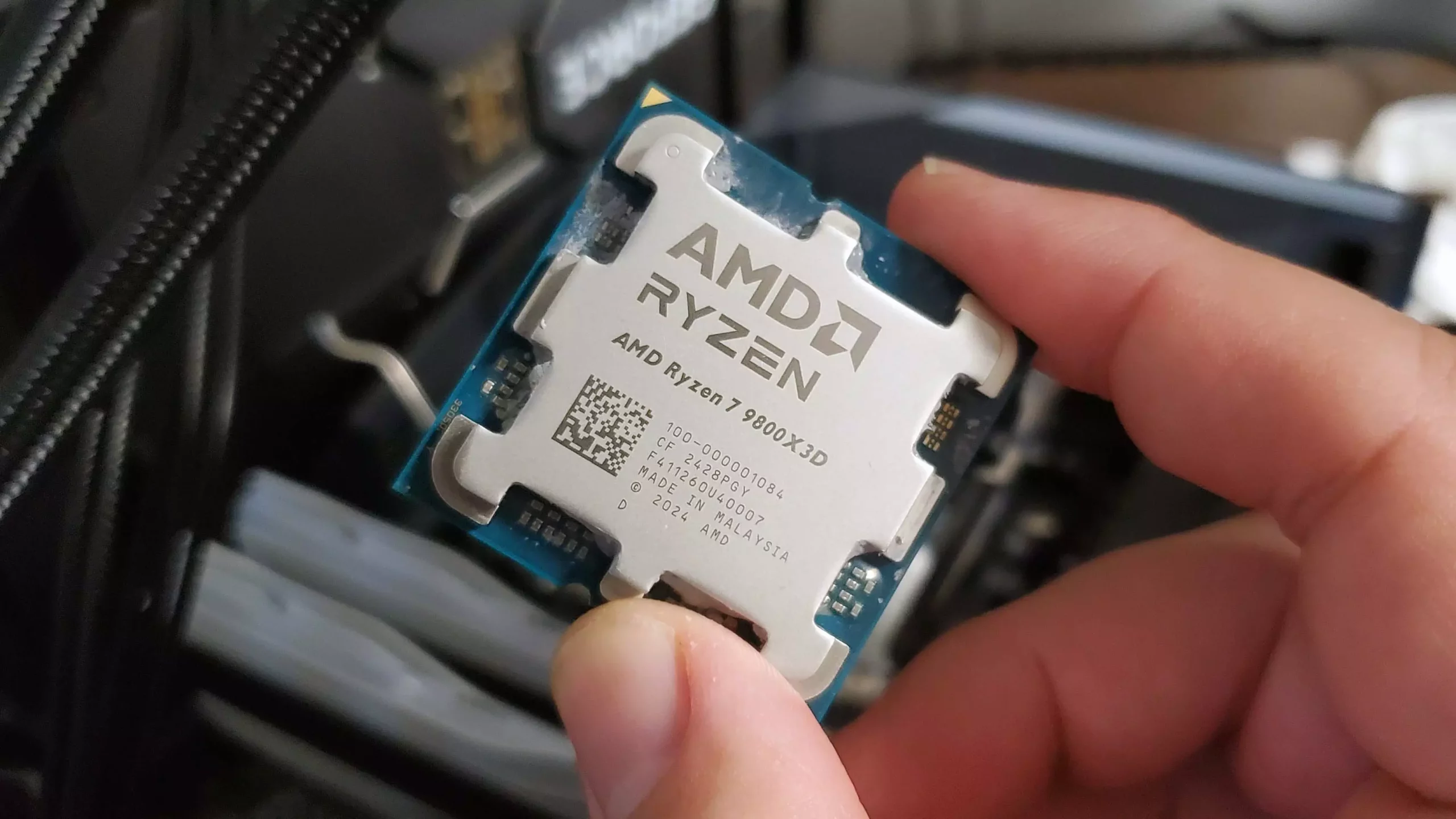
The Client and Gaming division alone generated over $3.7 billion, exemplifying how AMD’s offerings resonate with modern consumers. The introduction of Ryzen CPUs such as the 9800X3D and the Radeon RX 9070 XT graphics card has rejuvenated the PC building scene, drawing in gamers, creators, and even casual users eager for high-performance hardware. Furthermore, AMD’s growing footprint in the OEM world—highlighted by an upward surge in sales of Dell laptops powered by Ryzen chips—indicates a broader industry shift. OEMs are daring to pivot from Intel’s long-standing dominance, partly driven by consumer dissatisfaction with recent Intel releases and growing doubts about future Intel ambitions.
This shift demonstrates AMD’s strategic positioning to capitalize on the industry’s evolving landscape. It’s not just about next-generation hardware but about seizing opportunities created by uncertainty around competitors’ product pipelines. AMD’s success in the gaming segment is particularly noteworthy because it signifies more than just revenue; it signals confidence and a reputation for innovation that competitors will find increasingly difficult to match.
Challenges in the Data Center Arena and Political Hurdles
While AMD is celebrating substantial gains, it confronts a more complex reality in its data center division. Despite a 14% increase in revenue to $3.2 billion, the division reported an operating loss of $155 million. This discrepancy hints at underlying challenges that threaten to slow down AMD’s surging momentum. The primary culprits are geopolitical issues, notably export restrictions on the MI308 data center GPUs, which have led toInventory charges exceeding $800 million.
These restrictions reflect a broader geopolitical tension that transcends AMD’s control and threaten to stifle its growth in key markets. The company’s inability to fully access the Chinese market—an enormous growth opportunity—limits potential revenue and puts pressure on AMD to innovate around these barriers. The impact on inventory costs emphasizes the importance of navigating international policy landscapes, a task that becomes more critical as AMD attempts to scale its AI and data center ambitions.
Nevertheless, AMD remains optimistic about the future, projecting revenues soaring to $8.6 billion in Q3. This forecast underpins the company’s confidence in its product pipeline and strategic direction. Successful navigation of geopolitical hurdles, combined with the potential reintroduction of AI chips into restricted markets, could spark another significant revenue wave. However, it also underscores how external factors—beyond AMD’s control—can influence financial health, overshadowing its technological achievements.
The Race for Dominance: AMD’s Competitive Edge and Industry Implications
The landscape AMD is contending in is intensely competitive. Nvidia continues to dominate the data center segment with vastly larger revenues, making AMD’s positioning more of a foothold than a sprint. Despite this, AMD’s recent advancements demonstrate a clear intent to disrupt the status quo. Its chiplet architecture, for example, is a game-changer, offering scalable performance and cost advantages that can appeal across various markets.
More compelling, however, is AMD’s strategic focus on diversified segments. While Nvidia’s focus remains primarily on high-end AI and data center markets, AMD leverages its versatility to target gaming, consumer, and enterprise sectors simultaneously. The company’s bold predictions for Q3 reveal an outlook fueled by product launches, partnerships, and market share gains—factors that can propel it toward becoming a serious challenger.
Yet, the road ahead is fraught with obstacles. The global chip shortage, ongoing geopolitical tensions, and the rapidly evolving AI landscape mean AMD must stay innovative and agile. A critical factor will be whether AMD’s AI chips can once again start selling in China. If successful, the financial boost could be transformative, allowing AMD to close the gap with Nvidia and carve out a larger slice of the lucrative AI market.
In sum, AMD’s current trajectory demonstrates a mix of resilience, strategic risk-taking, and technological prowess. Its ability to adapt to external challenges while maintaining a focus on innovation could see it not only increasing revenues but fundamentally shifting industry power dynamics in the years to come. The next phase of AMD’s journey will determine whether it can leverage its momentum into sustained, industry-wide dominance or if geopolitical and competitive pressures will halt its ascent.